|
This web page is prepared for providing research materials of our travel-route-centered metro map project. |
Travel Guide Maps
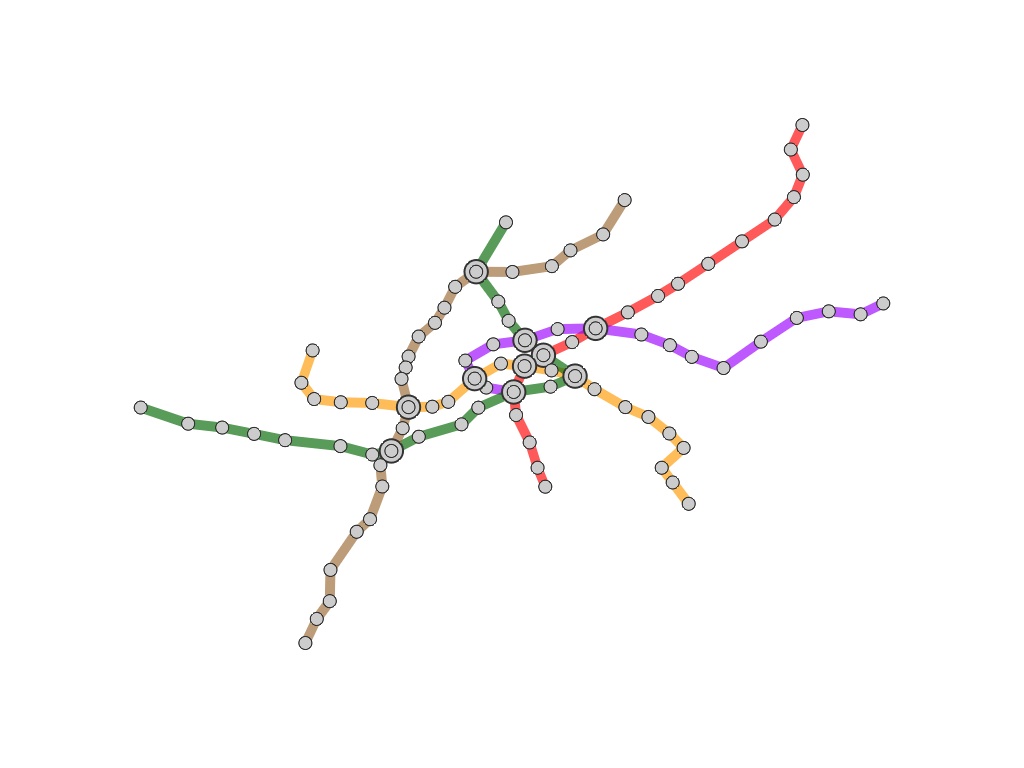
We find out that it is hard for metro users to follow and trace their interesting paths from the current
metro maps, especially for new comers in a city. When providing travel guides for a specific route in a metro
network, it is intuitive to place the route around the center of the map and annotate stations on the route
with thumbnail photographs. Recently, more and more metro companies also incorporate these ideas to create
friendly transportation maps for their system users. Nonetheless, existing methods do not offer an effective
means of customizing the network layout in order to accommodate such large annotation labels while preserving
its planar embedding. In this project, we present a new approach for designing the metro map layout in order
to annotate stations on a specific travel route with large annotation labels.
|
|
 |
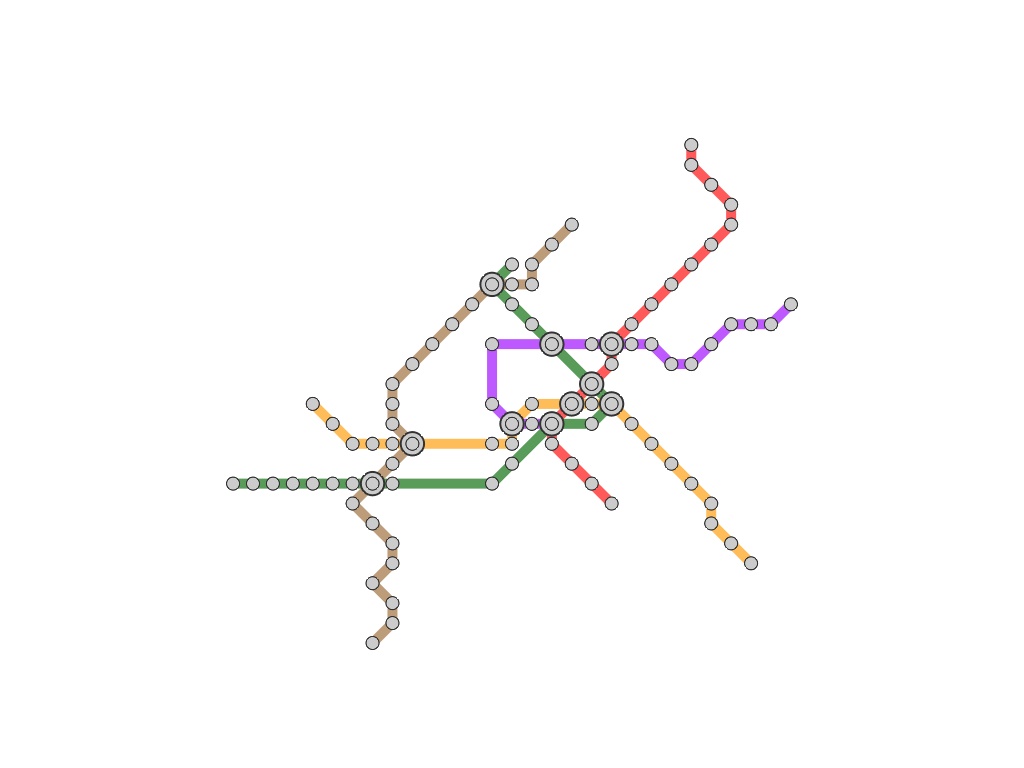
| (a) The path on original metro maps | (b) The path on our route-centered maps |
|
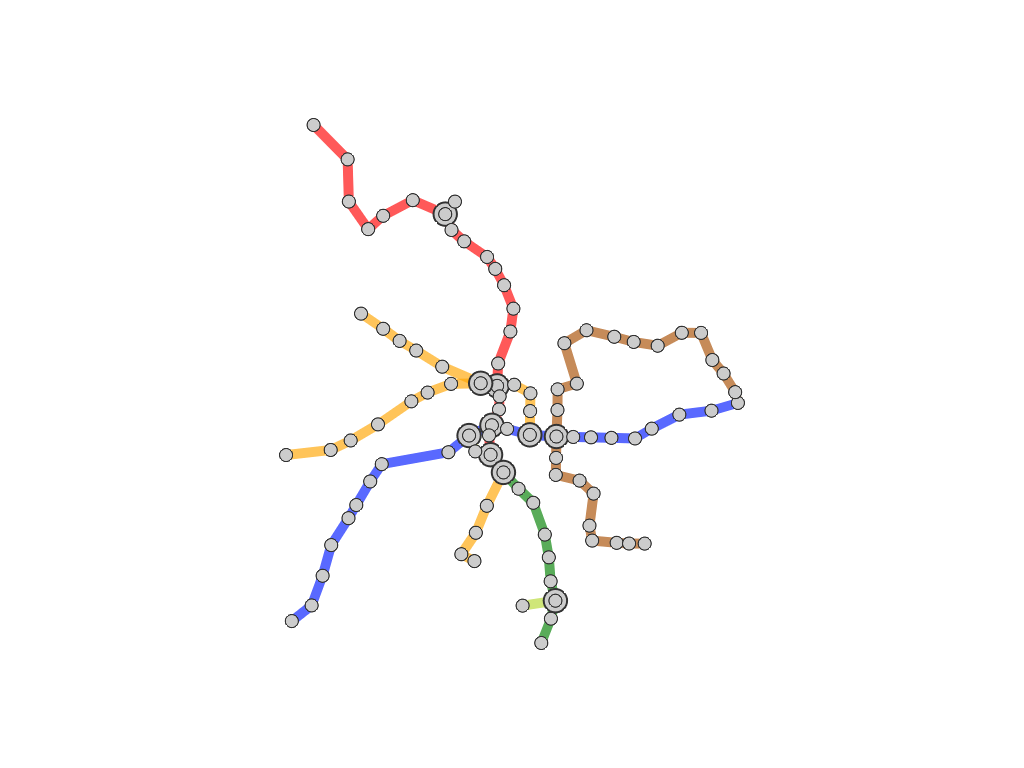
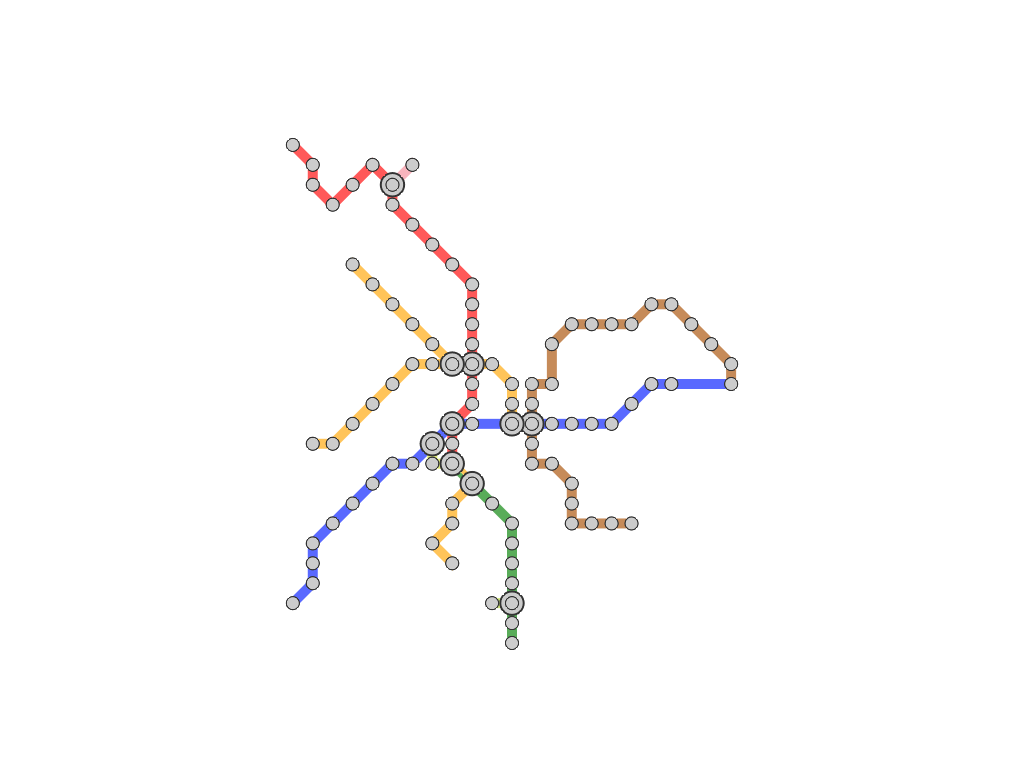
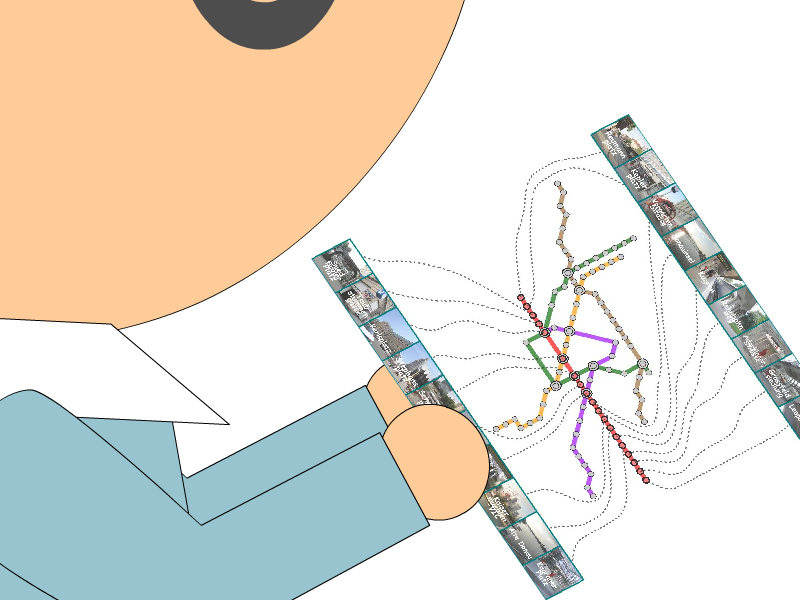
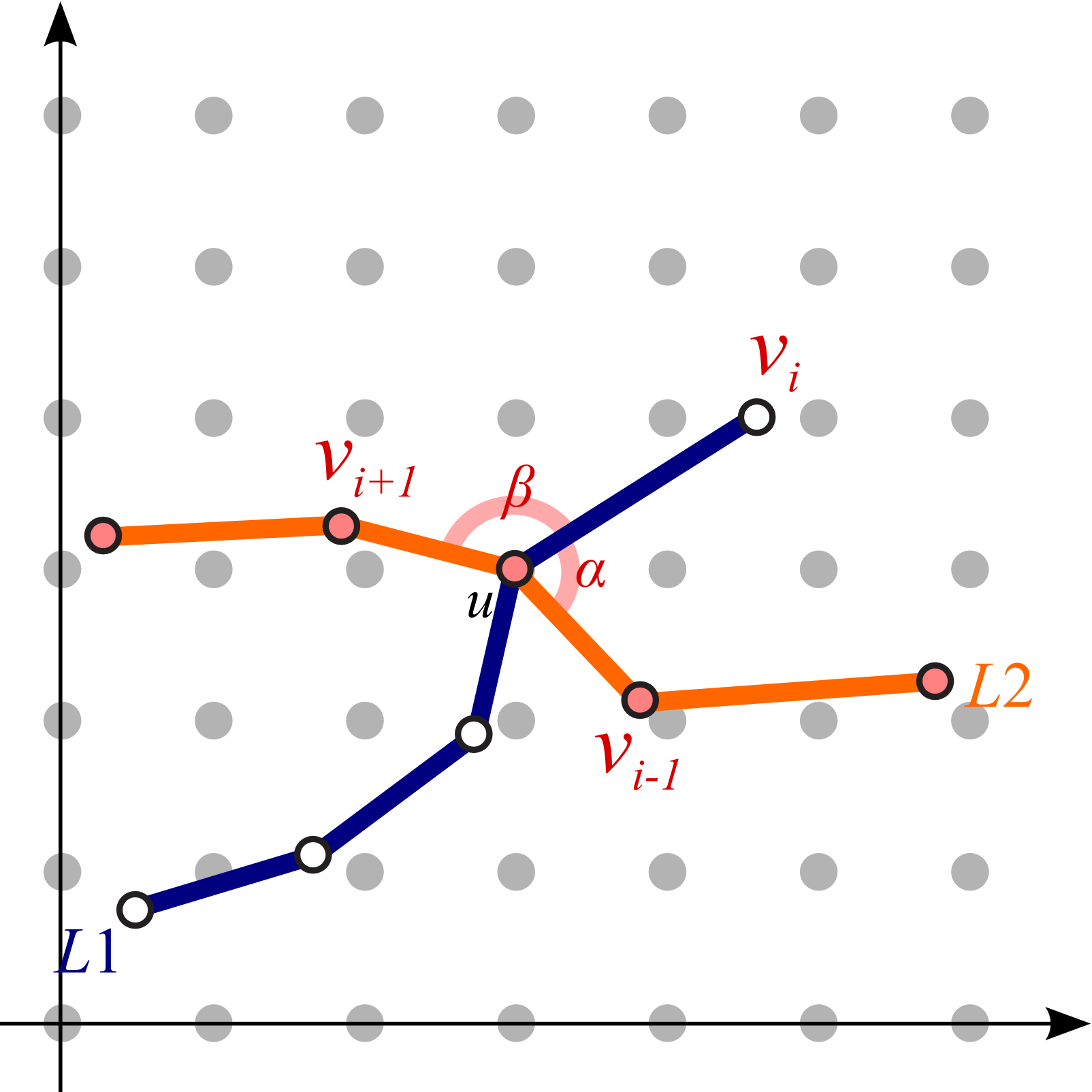
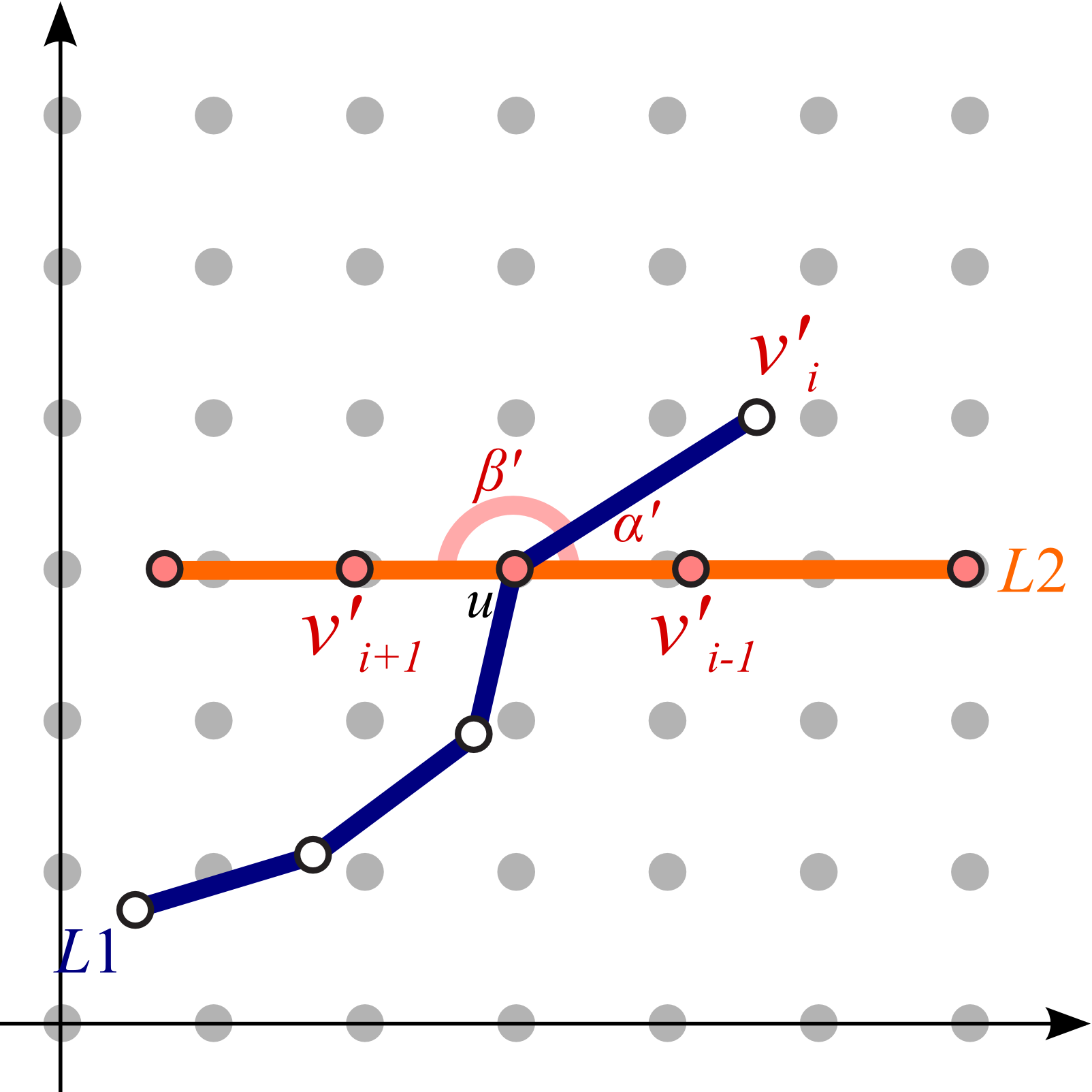
Our idea is to elongate the travel route to be straight along the centerline of the map so that we can systematically
annotate such stations with external labels. This is accomplished by extending the conventional mixed-integer programming
technique for computing octilinear layouts where orientations inherent to the metro line segments are plausibly rearranged.
Once the user-defined route is rearranged, we alleviate the angle gaps by propagating the changes in the edge
orientation on the route.
|
|
|
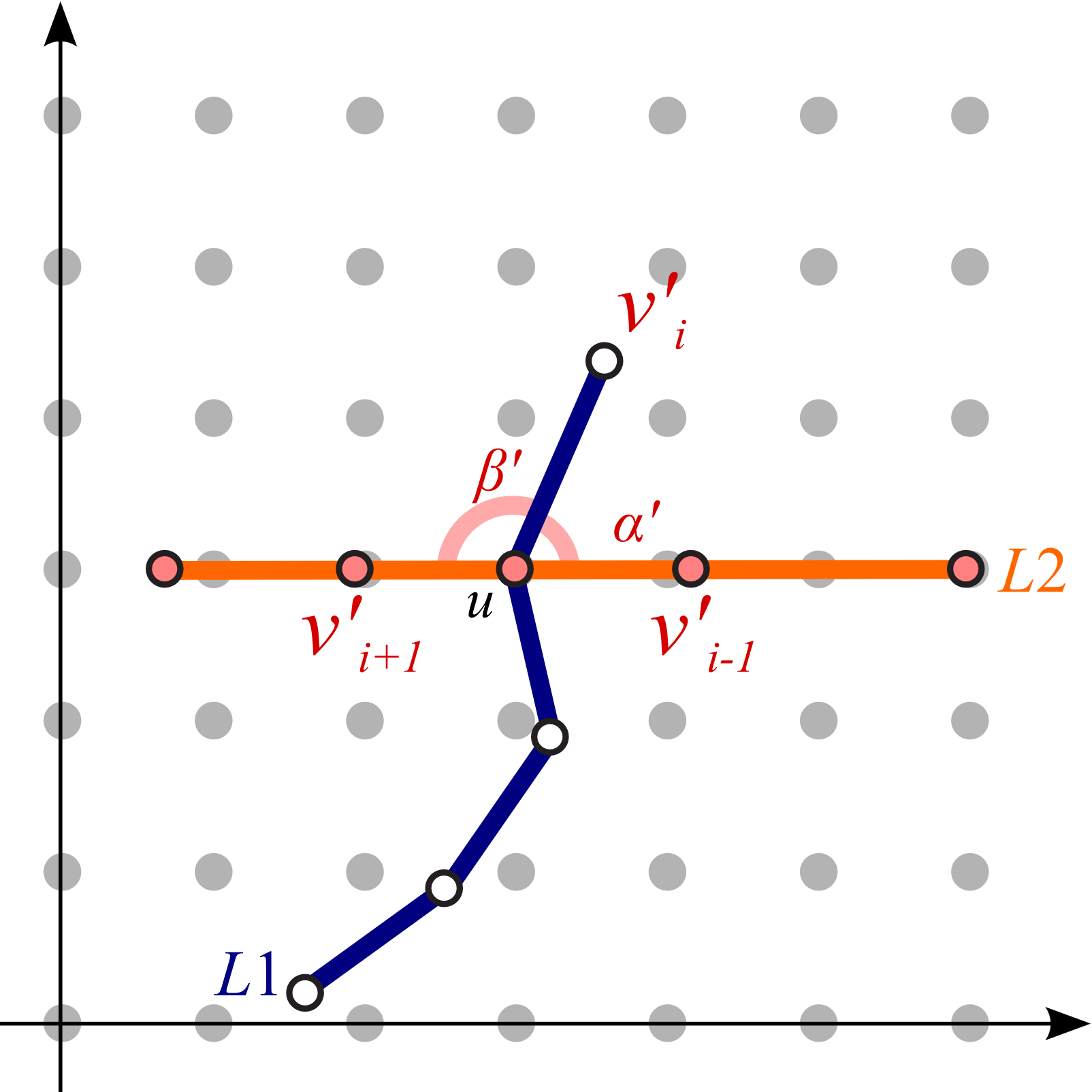 |
| (a) Original angles |
(b) Angles after straightening the path |
(c) Angles after propagation effect from the center line |
|
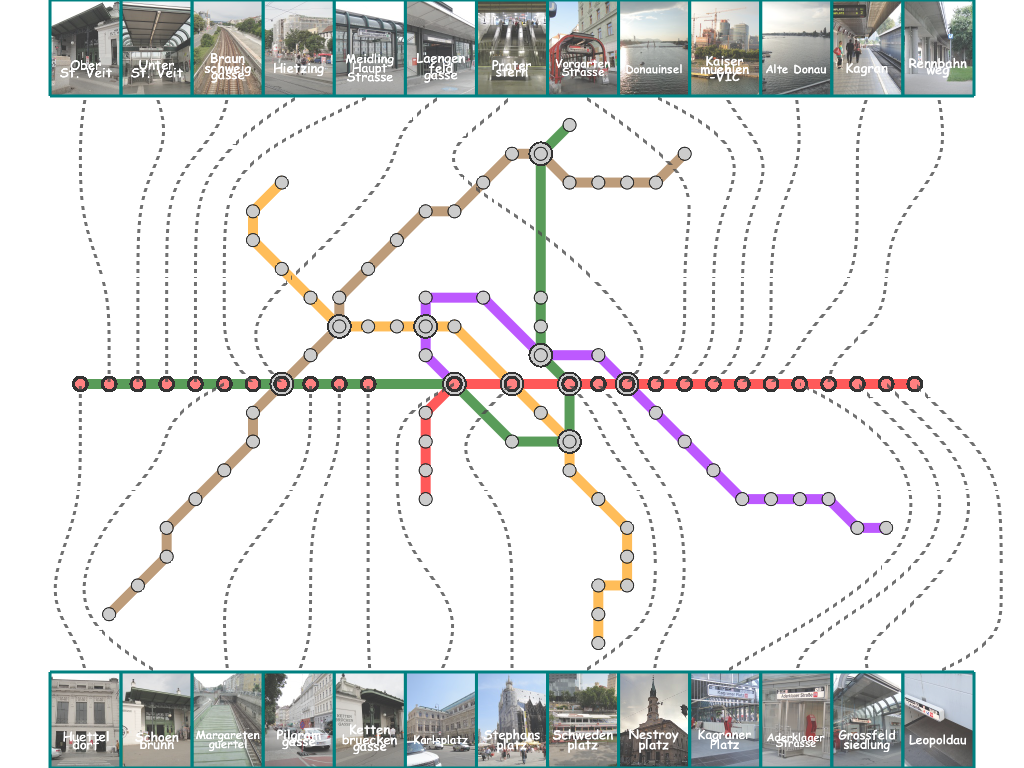
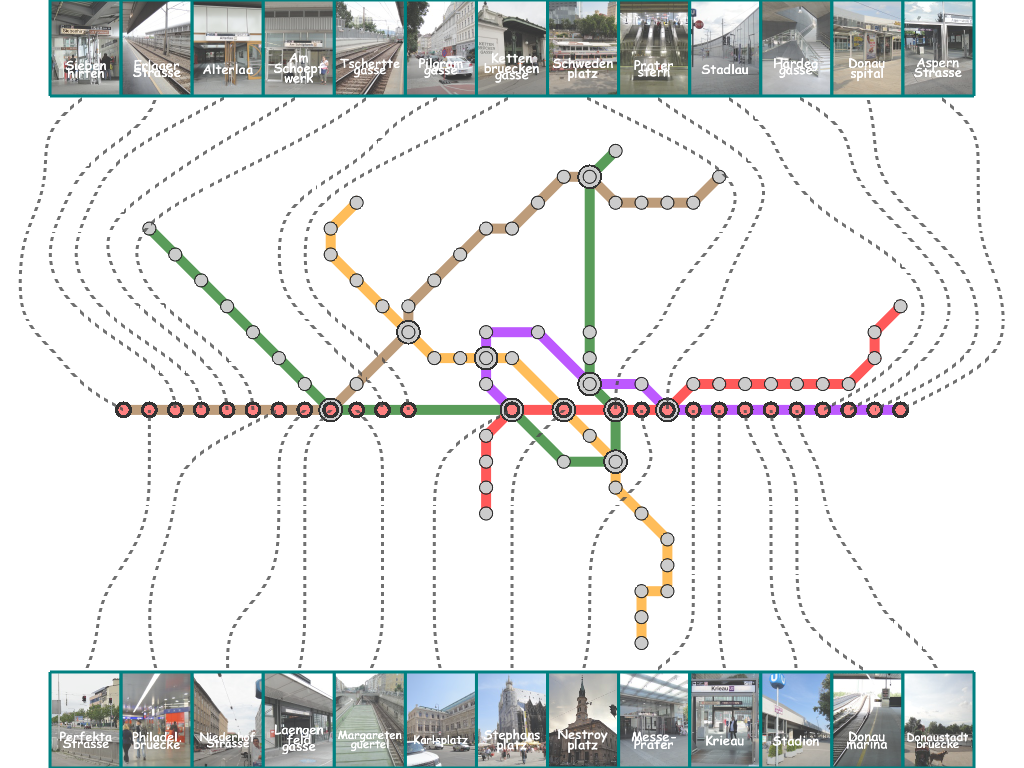
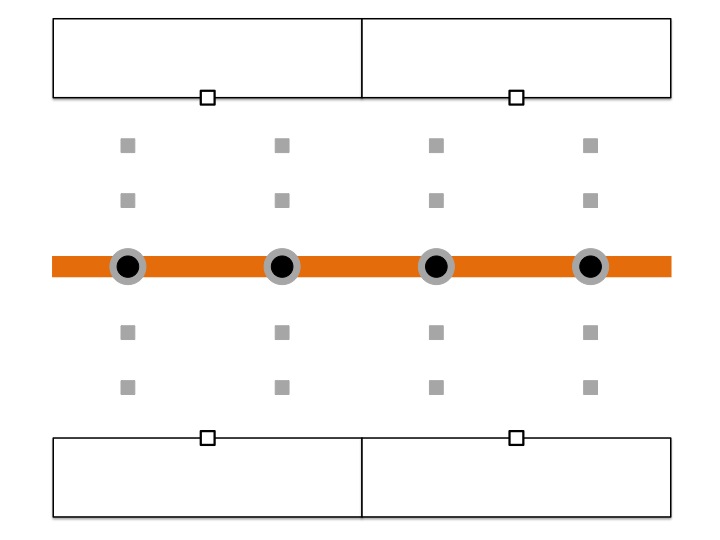
The stations are then connected with external labels through leaders while minimizing intersections with metro lines
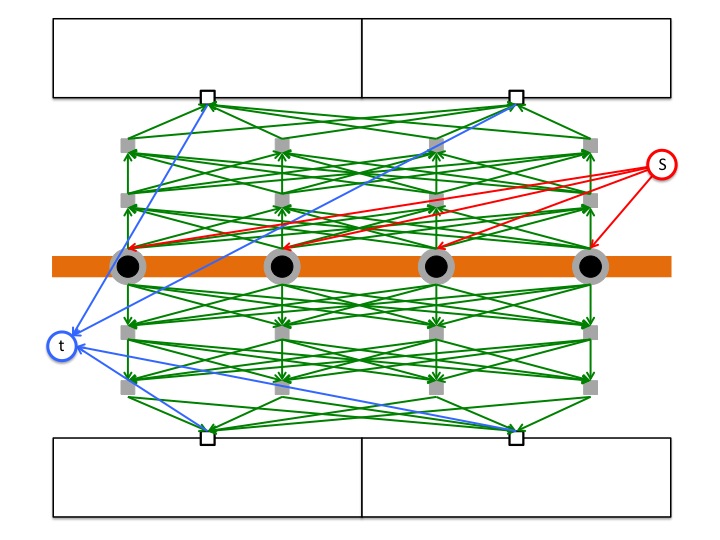
for enhancing visual clarity. We solve this problem by taking advantage of the concept of the min-cost max-flow problem.
We present several design examples of metro maps and user studies to demonstrate that the proposed aesthetic criteria
successfully direct viewers’ attention to specific travel routes.
|
|
|
 |
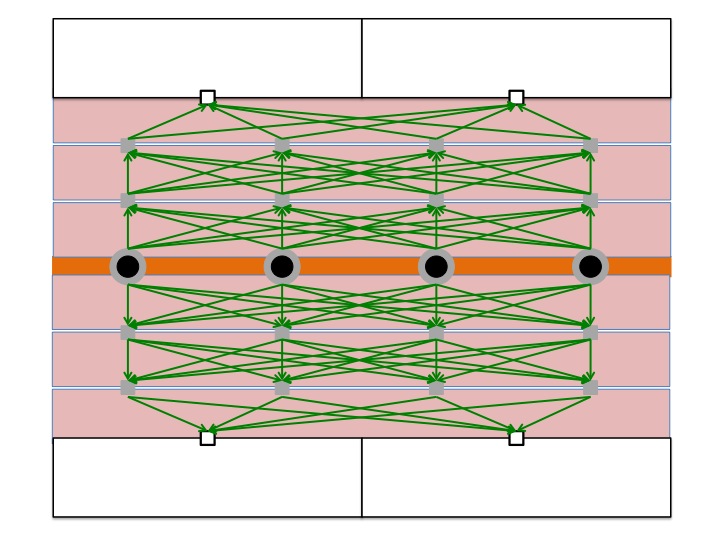
| (a) Locating intermediate points |
(b) Constructing complete bipartite graphs between each pair of horizontal adjacent row |
(c) Adding a source and a sink node to complete the construction |
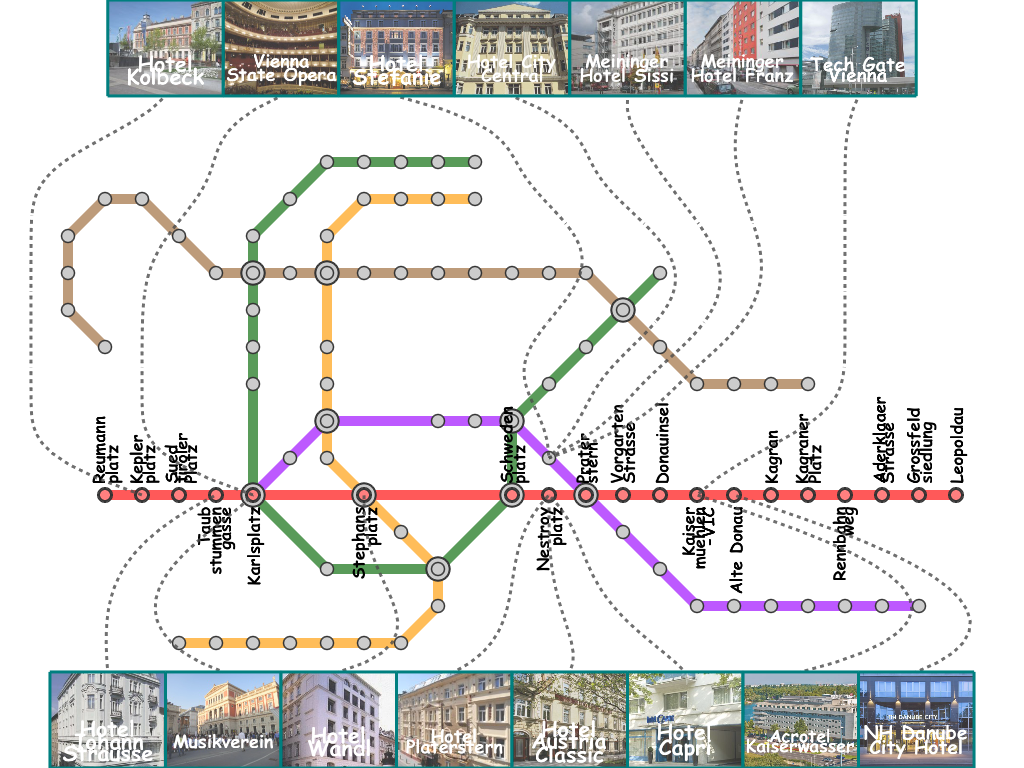
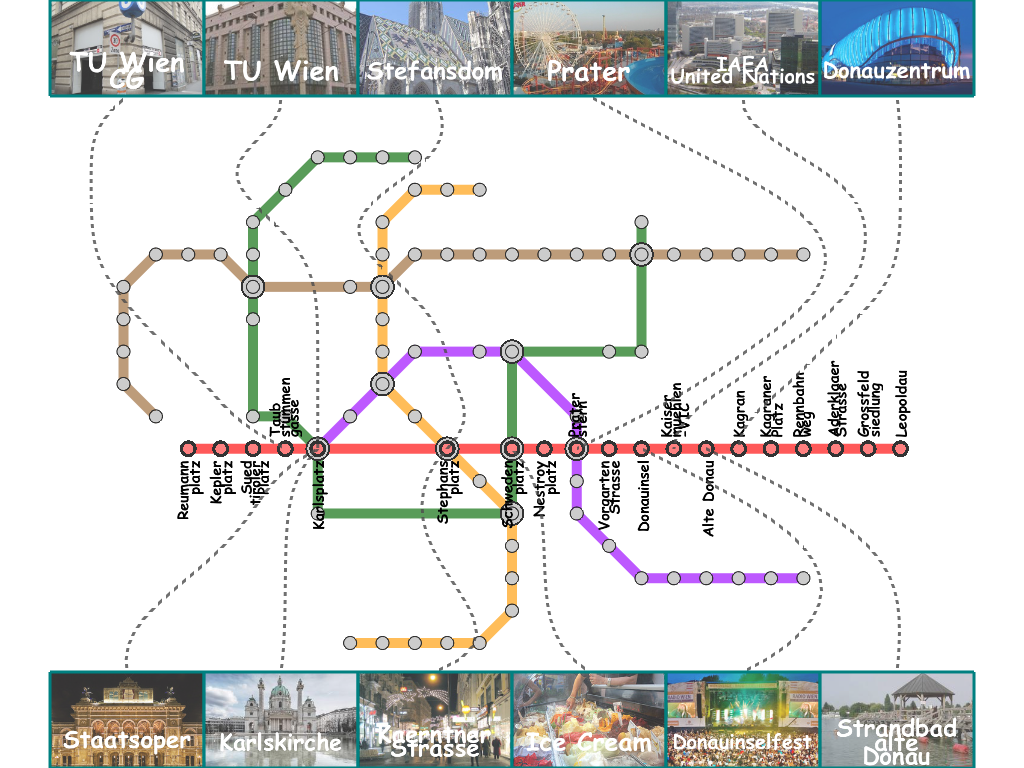
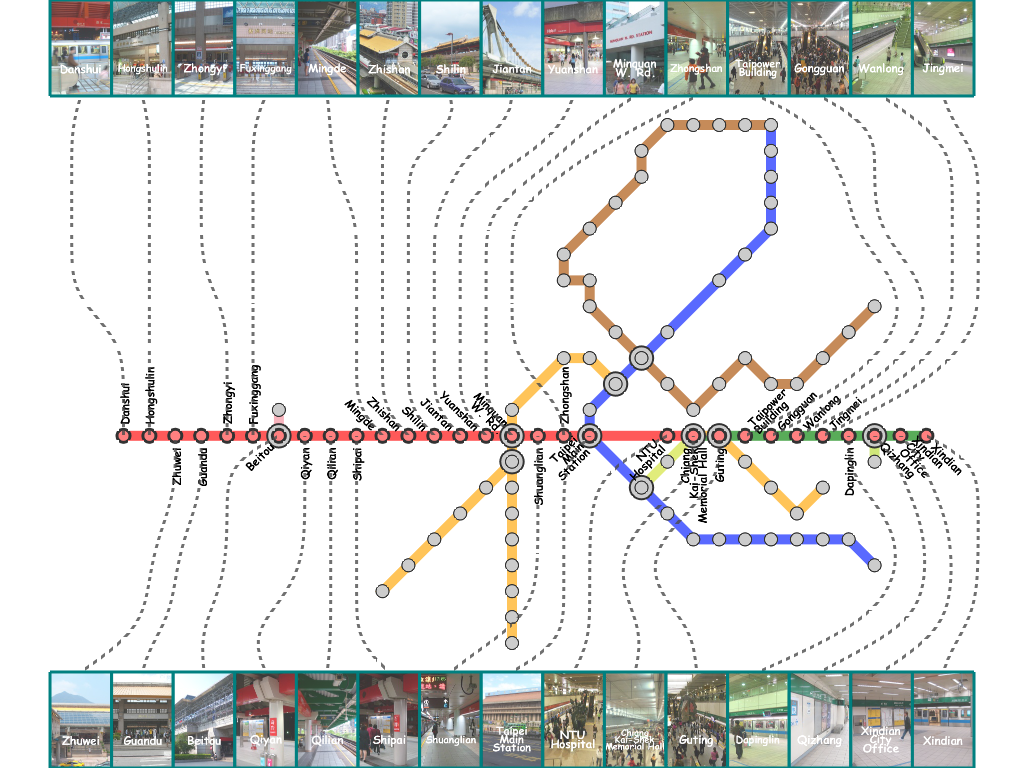
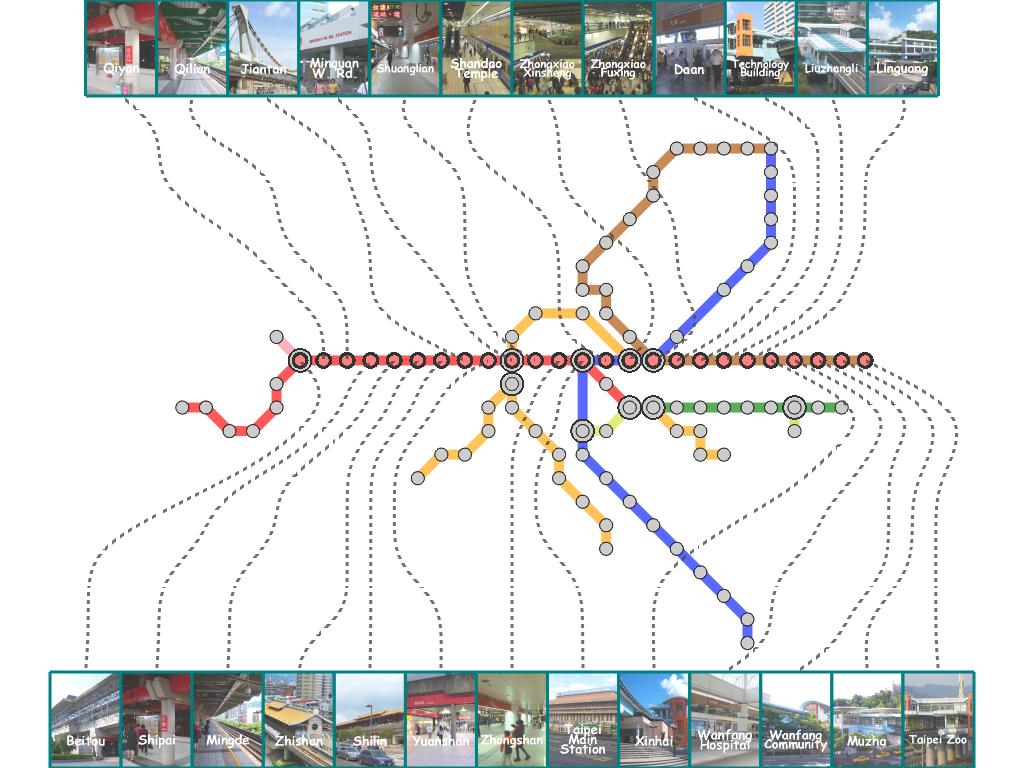
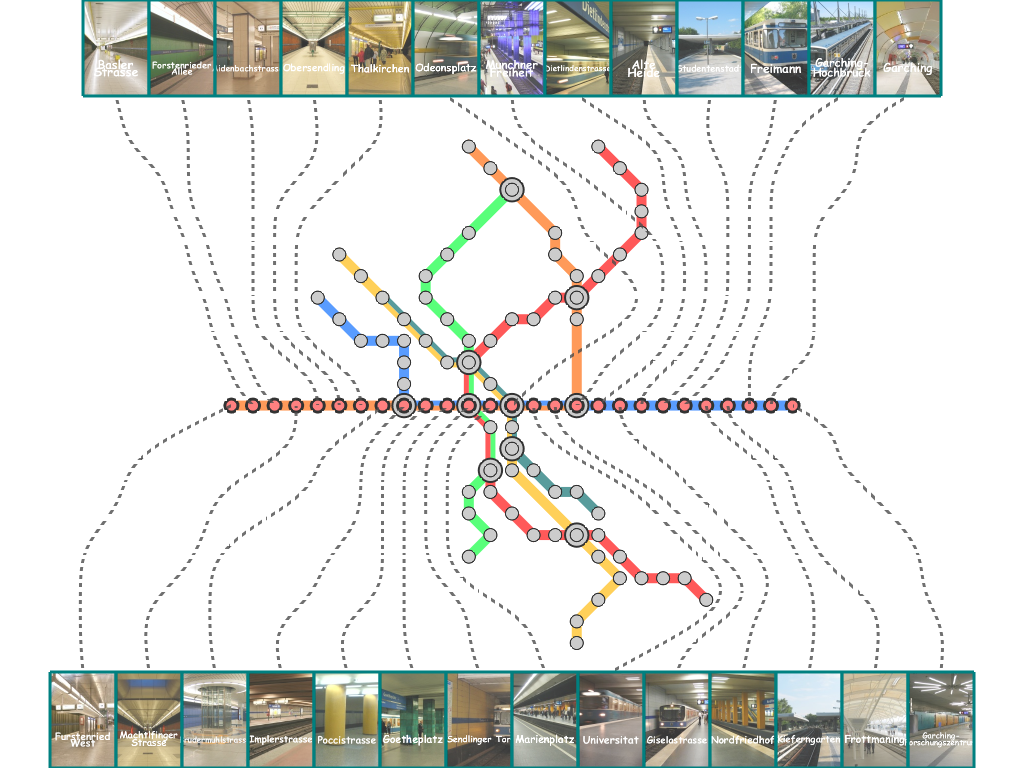
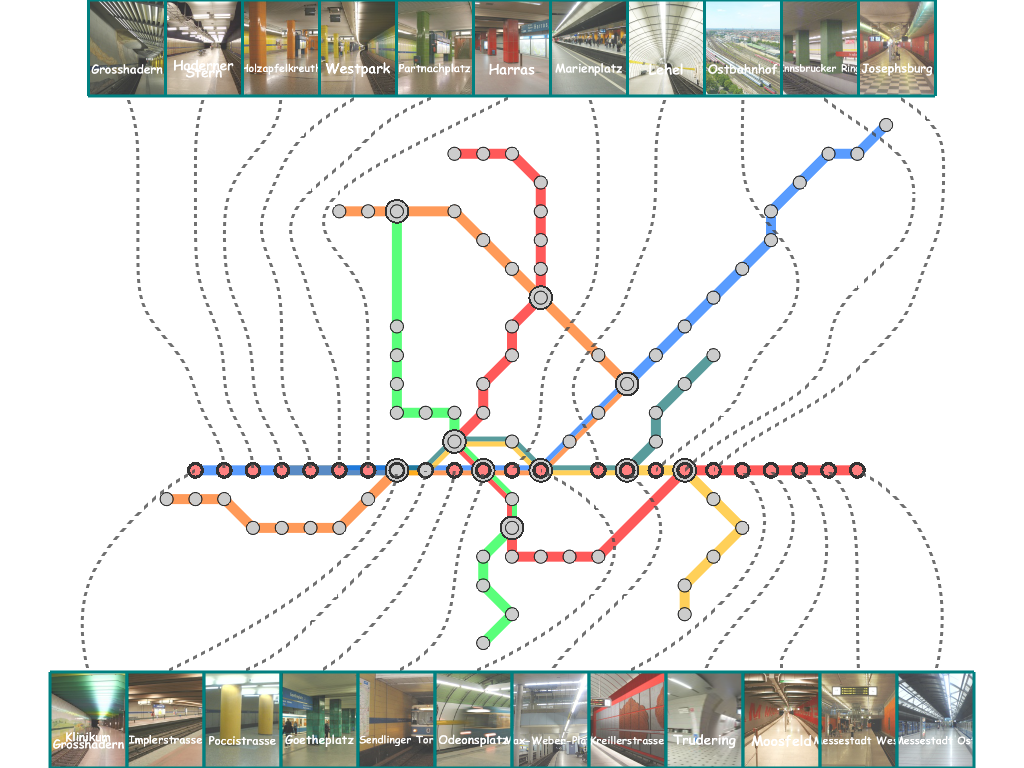
Results
Here, we present several results that are generated from our prototype system.
(You can click the thumbmail image for that of the original resolution.) |
Paper & VideoHsiang-Yun Wu, Shigeo Takahashi, Chun-Cheng Lin, and Hsu-Chun Yen, Travel-route-centered metro map layout and annotation, Computer Graphics Forum (Proceedings of the 14th Eurographics/IEEE Symposium on Visualization (EuroVis 2012), Vol. 31, No. 3, pp. 925-934, 2012. Paper-preprint (PDF, 12.2MB), Video(MOV, 27.1MB) |